The climate investments in the Build Back Better Act (BBBA) deliver significant value for American families, reducing our monthly energy bills and protecting us from energy volatility and inflation. These investments also improve health outcomes and create good-paying jobs, the majority of which cannot be automated or offshored. Indeed, it is precisely by delivering kitchen table benefits to all Americans — and particularly to those who need it the most — that this climate package enables us to make essential progress on our climate goals. Said simply, 42 percent of U.S. energy-related emissions come from our homes and the machines we use every day: the cars we drive, how we heat and cool our homes, how we heat our water, dry our clothes, and cook our meals. We stand no chance of staying inside of 1.5 degrees Celsius warming unless we electrify our lives.
We are at a pivotal moment where we have the opportunity to push forward legislation that will save households billions of dollars in energy bills, while building out the climate-safe future we need. This brief highlights key public-facing climate policies and their benefits to provide a sense of the catalytic power this legislation will have. Billions of dollars saved, millions of lives improved, no time to waste.
Key Takeaways

Consumer-Facing Climate Investments
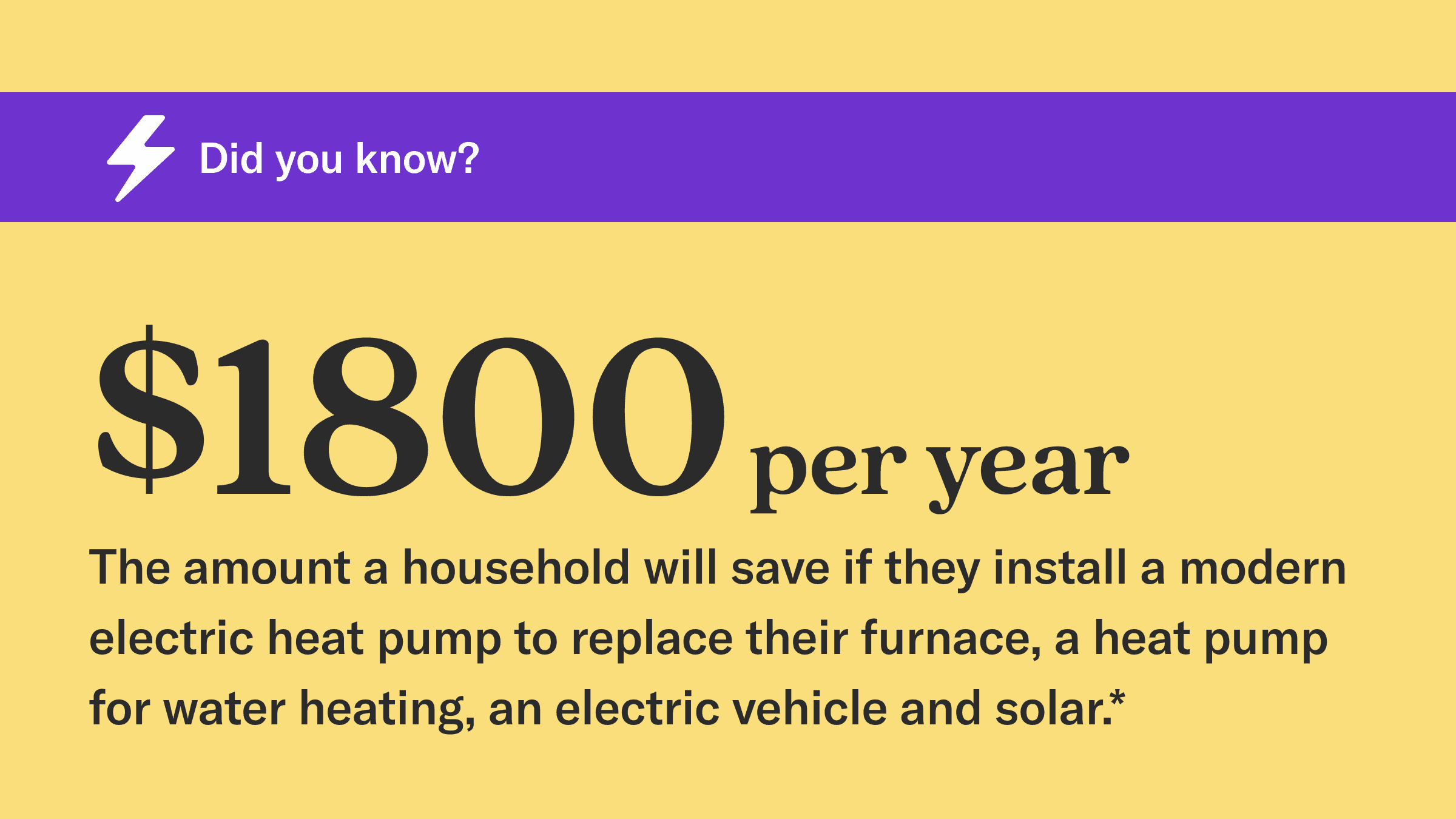
Kitchen Table Climate Investments: Approximately $140 billion, including clean energy tax credits but not including public housing investments.
Per the Justice40 Initiative: At least $56 billion (40%) of these investments will go to disadvantaged communities. An additional $69 billion are included in investments in public housing and healthy housing funding for these communities.
Housholds reached: At least 25 million.
Emissions saved in 2030: 200 million metric tons (MMT) of CO2e.
Industries Covered:
Renewable energy: rooftop and community solar, battery storage.
Transportation: Electric vehicles and charging infrastructure.
Buildings: Energy efficiency, including efficient electric appliances, geothermal.
The source for this figure, which fluctuates slightly over time, comes from the EPA's 2023 Annual Greenhouse Gas Inventory, which has data from 2021. We start with Table 2-10 (Raw-Economic Sector): U.S. Greenhouse Gas Emissions Allocated to Economic Sectors (MMT CO2 Eq. and Percent of Total in 2021), then distribute electricity among the economic sectors using Table 2-12: U.S. Greenhouse Gas Emissions by Economic Sector and Gas with Electricity-Related Emissions Distributed (MMT CO2 Eq.) and Percent of Total in 2021. We calculate the percent of energy-related emissions and verify that it matches Table 2-3: Recent Trends in U.S. Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Sinks by IPCC Sector/Category (MMT CO2 Eq.) Unlike the EPA, we don't include "Non-Energy Use of Fuels" as energy-related. We then calculate the percent of emissions attributable to households, which can require breaking a line item like transportation emissions from combusting fossil fuels into household and non-household pieces. We also break the emissions from fossil fuel production & transportation, which are part of the industrial sector, into their household and non-household pieces.